Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt
IGBT Driver Calculation Power. Guru. This article provides information on the determination of driver output performance for switching IGBTs. The information given in this application note contains tips only and does not constitute complete design rules the information is not exhaustive. The responsibility for proper design remains with the user. Introduction. One key component of every power electronic system is besides the power modules themselves the IGBT driver, which forms the vital interface between the power transistor and the controller. For this reason, the choice of driver and thus the calculation of the right driver outputpower are closely linked with the degree of reliability of a converter solution. Insufficient driver power or the wrong choice of driver may result in module and driver malfunction. IGBT-gate-driver_5F00_part1_5F00_fig1.png' alt='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' title='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' />ON Semiconductor supplies MOSFET drivers and IGBT drivers for low side, high side, and halfbridge drive circuits. This article provides information on the determination of driver output performance for switching IGBTs. The information given in this application note contains tips. The A4900 is a highvoltage, highspeed, power IGBT or MOSFET driver providing three independent halfbridge channels for threephase applications. Many integrated circuits have undocumented features or abilities. This is one of them. The TLC555 output pin 3 can sink a 100mA load to 1. V. The open d. IGBT is a three terminal power semiconductor switch. Both Power BJT and Power MOSFET have their own pros and cons. IGT. Take note from the power management experts at IR. Our comprehensive library of Application Notes will help you optimize your design using IRs solutions. Littelfuse, Inc. 1 www. Application TVS Diode Protection for VFDsIGBT Inverters Introduction In virtually all industrial control systems. Gate Charge Curve. The switching behaviour turn on and turn off of an IGBT module is determined by its structural, internal capacitances charges and the internal and outer resistances. When calculating the output power requirements for an IGBT driver circuit, the key parameter is the gate charge. This gate charge is characterised by the equivalent input capacitances CGC and CGE. IGBT Capacitances. The following table explains the designation of the capacitances. In IGBT data sheets these capacitances are specified as voltage dependent low signal capacitances of IGBTs in the off state. One of the serious problems in relay operated circuits is the relay clicking or chattering during the onoff of the relay driver transistor. This problem i. 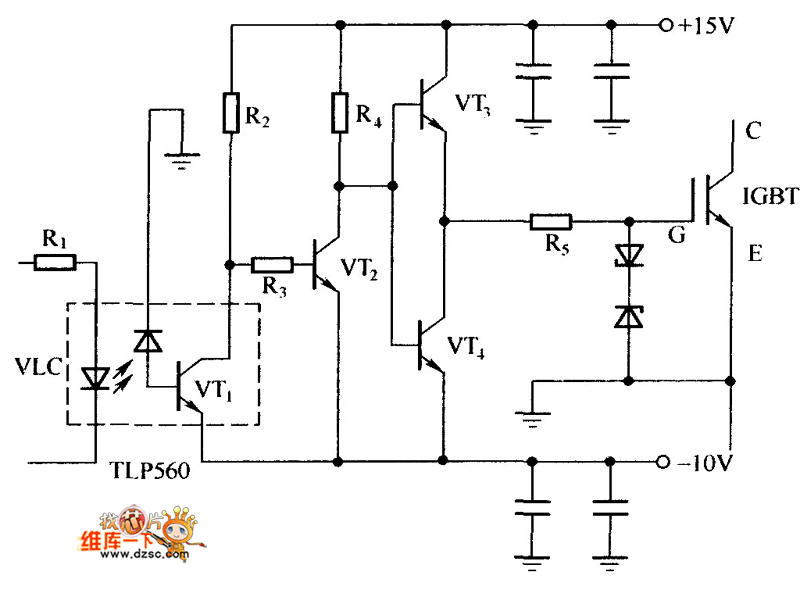 The capacitances are independent of temperature, but dependent on the collector emitter voltage, as shown in the following curve. This dependency is substantially higher at a very low collector emitter voltage. Parasitic and Low Signal Capacitances. Capacitances. Designation. CGEGate emitter capacitance. CCECollector emitter capacitance. CGCGate collector capacitanceMiller capacitanceLow Signal. Capacitances. Designation. Input capacitance. Reverse transfer capacitance. Output capacitance. AFISJUnJkpM/T8Lqr0i7PyI/AAAAAAAAA3k/7QyD-eBkqNE/s1600/4a-high-speed-low-side-gate-driver-1337963926_525_259.PNG' alt='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' title='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' />
The capacitances are independent of temperature, but dependent on the collector emitter voltage, as shown in the following curve. This dependency is substantially higher at a very low collector emitter voltage. Parasitic and Low Signal Capacitances. Capacitances. Designation. CGEGate emitter capacitance. CCECollector emitter capacitance. CGCGate collector capacitanceMiller capacitanceLow Signal. Capacitances. Designation. Input capacitance. Reverse transfer capacitance. Output capacitance. AFISJUnJkpM/T8Lqr0i7PyI/AAAAAAAAA3k/7QyD-eBkqNE/s1600/4a-high-speed-low-side-gate-driver-1337963926_525_259.PNG' alt='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' title='Gate Driver Circuit For Igbt' /> Cies, Coes, Cres fVCEThe figures below show simplified the gate charge waveforms VGE ft, IGft, VCEft, and ICft during turn on of the IGBT. The turn on process can be divided into three stages. These are charging of the gate emitter capacitance, charging of the gate collector capacitance and charging of the gate emitter capacitance until full IGBT saturation. To calculate the switching behaviour and the driver, the input capacitances may only be applied to a certain extent. A more practical way of determining the driver output power is to use the gate charge characteristic given in the IGBT data sheets. This characteristic shows the gate emitter voltage VGE over the gate charge QG. The gate charge increases in line with the current rating of IGBT modules. The gate charge is also dependent on the DC Link voltage, albeit to a lesser extent. At higher operation voltages the gate charge increases due to the larger influence of the Miller capacitance. In most applications this effect is negligible. Title AND9052 IGBT Gate Drive Considerations Author ffgztc Subject The IGBT transistor is a much more complex structure than either a MOSFET or a Bipolar. Power conversion efficiency and reduction of power loss is the main target of power electronics. The development of 3Level power converters realized by neutral. Simplified Gate Charge Waveforms. Gate Charge Characteristict. The gate current IG charges the input capacitance CGE and the gate emitter voltage VGE rises to VGEth. Depending on the gate resistor, several amperes may be running in this state. As VGE is still below VGEth, no collector current flows during this period and VCE is maintained at VCC level. As soon as VGE passes VGEth, the IGBT turn on process starts. IC begins to increase to reach the full load current I Cload , which is valid for an ideal free wheeling diode shown in the simplified waveform. For a real free wheeling diode, IC exceeds ICload. Wardriving And Wireless Penetration Testing Ebook. This is because a reverse recovery curre nt, which flows in reverse direction, is added to ICload. Since the free wheeling diode is still conducting current at the beginning of section t. Remington Model 870 Shotgun Gunsmithing Manual. VCE will not dro p. VGE reaches the plateau voltage VGEpl. VGE maintains VGEpl. When the free wheeling diode is turned off, VCE starts to drop rapidly and dv. CEdt is high. t. While VCE is decreasing to reach on state value VCEsat, the Miller capacitance CGC increases as the voltage decreases and is charged by IG. VGE still remains on a plateau, which is VGEpl level. At the beginning of section t. IGBT is fully turned on. The charge conducted to CGE induces an exponential increase in VGE up to the gate control voltage VGEon. IG ends with an exponential fade out and VCE reaches VCEsat level. During turn off the processes described are running in reverse direction. The charge has to be removed from the gate. Measuring the Gate Charge. A simplified test circuit that can be used to measure the gate charge is shown in the following table. The gate is supplied by a constant gate current. Furthermore, a pulse constant collector current is applied. The constant gate current causes the measured waveform VGE ft to be equivalent to VGE fQG due to QG IG x t. The document IEC 6. Ed. 2 Semiconductor Devices Discrete Devices Part 9 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors IGBTs describes the gate charge test method. Basis Test Circuit for Gate Charge Measurement. Waveform VGE ft VGE fQGDetermining the Gate Charge. The gate charge per pulse needed to drive the IGBT can be determined using the gate charge characteristic diagram, which shows gate emitter voltage over gate charge. The total gate charge can be read out by taking into account the amplitude of the applied gate voltage, i. VGon to turn off gate voltage VGoff. If the gate charge curve is given in the positive quadrant only, the gate charge amplitude can be read out by extrapolation, as shown in the following table. The bright green represents the area of a diagram given in the IGBT data sheet. A parallel adjustment of the bright green area along the gate charge curve into the negative quadrant up to VGoff allows for the amplitude of the gate charge to be determined. Gate charge characteristic. Extrapolation Method. Another method for determining the gate charge uses the input capacitance Cies and a special factor instead of the gate charge curve. The value for Cies is given in the IGBT data sheet. The necessary gate charge or the charging energy per pulse must be available at the right time. This can only be achieved by using low impedance, low inductance output capacitors at the driver output stage. The size of the capacitors is indicated by the calculated value QG. The gate charge is the basic parameter used to determine driver output power and gate current. Gate Charge Calculation with Cies Method. The gate charge can be expressed aswhere the gate capacitance factor kc can be roughly calculated aswhere QGds is the value specified in the IGBT data sheet, and VGon as well as VGoff are the gate voltages applied to QGds. Thus, the alternative gate charge calculation is as follows Please note This method is not entirely accurate and should only be used if nogate charge curve is available. Driver Output Power. The individual power of each internal supply needed to drive the IGBT can be found as a function of the intended switching frequency and the energy which has to be used to charge and discharge the IGBT. Calculation of Driver Output Power per Channel. Power can be expressed as. Substituting the driver output power per channel is Rough calculation of driver power usinf the Cies method Gate Current. One of the key requirements for IGBT driver circuits is that enough current be supplied to charge and discharge the input capacitances of the IGBT and thus to switch the IGBT on and off.
Cies, Coes, Cres fVCEThe figures below show simplified the gate charge waveforms VGE ft, IGft, VCEft, and ICft during turn on of the IGBT. The turn on process can be divided into three stages. These are charging of the gate emitter capacitance, charging of the gate collector capacitance and charging of the gate emitter capacitance until full IGBT saturation. To calculate the switching behaviour and the driver, the input capacitances may only be applied to a certain extent. A more practical way of determining the driver output power is to use the gate charge characteristic given in the IGBT data sheets. This characteristic shows the gate emitter voltage VGE over the gate charge QG. The gate charge increases in line with the current rating of IGBT modules. The gate charge is also dependent on the DC Link voltage, albeit to a lesser extent. At higher operation voltages the gate charge increases due to the larger influence of the Miller capacitance. In most applications this effect is negligible. Title AND9052 IGBT Gate Drive Considerations Author ffgztc Subject The IGBT transistor is a much more complex structure than either a MOSFET or a Bipolar. Power conversion efficiency and reduction of power loss is the main target of power electronics. The development of 3Level power converters realized by neutral. Simplified Gate Charge Waveforms. Gate Charge Characteristict. The gate current IG charges the input capacitance CGE and the gate emitter voltage VGE rises to VGEth. Depending on the gate resistor, several amperes may be running in this state. As VGE is still below VGEth, no collector current flows during this period and VCE is maintained at VCC level. As soon as VGE passes VGEth, the IGBT turn on process starts. IC begins to increase to reach the full load current I Cload , which is valid for an ideal free wheeling diode shown in the simplified waveform. For a real free wheeling diode, IC exceeds ICload. Wardriving And Wireless Penetration Testing Ebook. This is because a reverse recovery curre nt, which flows in reverse direction, is added to ICload. Since the free wheeling diode is still conducting current at the beginning of section t. Remington Model 870 Shotgun Gunsmithing Manual. VCE will not dro p. VGE reaches the plateau voltage VGEpl. VGE maintains VGEpl. When the free wheeling diode is turned off, VCE starts to drop rapidly and dv. CEdt is high. t. While VCE is decreasing to reach on state value VCEsat, the Miller capacitance CGC increases as the voltage decreases and is charged by IG. VGE still remains on a plateau, which is VGEpl level. At the beginning of section t. IGBT is fully turned on. The charge conducted to CGE induces an exponential increase in VGE up to the gate control voltage VGEon. IG ends with an exponential fade out and VCE reaches VCEsat level. During turn off the processes described are running in reverse direction. The charge has to be removed from the gate. Measuring the Gate Charge. A simplified test circuit that can be used to measure the gate charge is shown in the following table. The gate is supplied by a constant gate current. Furthermore, a pulse constant collector current is applied. The constant gate current causes the measured waveform VGE ft to be equivalent to VGE fQG due to QG IG x t. The document IEC 6. Ed. 2 Semiconductor Devices Discrete Devices Part 9 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors IGBTs describes the gate charge test method. Basis Test Circuit for Gate Charge Measurement. Waveform VGE ft VGE fQGDetermining the Gate Charge. The gate charge per pulse needed to drive the IGBT can be determined using the gate charge characteristic diagram, which shows gate emitter voltage over gate charge. The total gate charge can be read out by taking into account the amplitude of the applied gate voltage, i. VGon to turn off gate voltage VGoff. If the gate charge curve is given in the positive quadrant only, the gate charge amplitude can be read out by extrapolation, as shown in the following table. The bright green represents the area of a diagram given in the IGBT data sheet. A parallel adjustment of the bright green area along the gate charge curve into the negative quadrant up to VGoff allows for the amplitude of the gate charge to be determined. Gate charge characteristic. Extrapolation Method. Another method for determining the gate charge uses the input capacitance Cies and a special factor instead of the gate charge curve. The value for Cies is given in the IGBT data sheet. The necessary gate charge or the charging energy per pulse must be available at the right time. This can only be achieved by using low impedance, low inductance output capacitors at the driver output stage. The size of the capacitors is indicated by the calculated value QG. The gate charge is the basic parameter used to determine driver output power and gate current. Gate Charge Calculation with Cies Method. The gate charge can be expressed aswhere the gate capacitance factor kc can be roughly calculated aswhere QGds is the value specified in the IGBT data sheet, and VGon as well as VGoff are the gate voltages applied to QGds. Thus, the alternative gate charge calculation is as follows Please note This method is not entirely accurate and should only be used if nogate charge curve is available. Driver Output Power. The individual power of each internal supply needed to drive the IGBT can be found as a function of the intended switching frequency and the energy which has to be used to charge and discharge the IGBT. Calculation of Driver Output Power per Channel. Power can be expressed as. Substituting the driver output power per channel is Rough calculation of driver power usinf the Cies method Gate Current. One of the key requirements for IGBT driver circuits is that enough current be supplied to charge and discharge the input capacitances of the IGBT and thus to switch the IGBT on and off.